Ijraset Journal For Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology
- Home / Ijraset
- On This Page
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Conclusion
- References
- Copyright
Safeguarding Nations from Online News Threats Using Hybrid Technique
Authors: N. Bhagyalakshmi, V. Keerthi Priya, P. Divya, V. Rebka
DOI Link: https://doi.org/10.22214/ijraset.2024.58781
Certificate: View Certificate
Abstract
The internet provides a potent platform for individuals to express their opinions and emotions, facilitated by widespread smartphone usage and high internet accessibility. However, monitoring these online sentiments is crucial for identifying any extreme emotions that could potentially pose risks to national security. To address this, a new theoretical framework has been proposed, which combines a lexicon-based approach with machine learning techniques in the digital realm. This hybrid framework incorporates Decision Tree, Naive Bayes, and Support Vector Machine classifiers to predict political security threats. Through experimentation, it was found that the combination of a lexicon-based approach with the Decision Tree classifier yielded the highest performance score in predicting these threats. Natural Language Processing (NLP) techniques are employed for opinion mining within this framework.
Introduction
I. INTRODUCTION
In today's world, the internet has become an indispensable aspect of national security, with cyber threats being identified as significant concerns by the US Intelligence Community. These threats are now regarded on par with traditional security risks like terrorism, highlighting the evolving nature of security challenges. However, safeguarding a nation has become increasingly intricate due to factors such as the overwhelming volume of data, the abundance of information available online, and the rampant spread of misinformation and fake news. These factors collectively pose a persistent risk to national security. One crucial aspect that this project addresses is the relationship between online sentiments, opinions, and security threats. It underscores the importance of swiftly detecting and intervening in response to emerging threats identified through online emotions and opinions. Despite the evident correlation between emotions expressed online and security threats, there is currently a notable absence of a comprehensive assessment framework within the field of national security. This project aims to bridge this gap by pioneering a new approach to predicting political threats that are linked to online emotions. Recognizing the critical role of emotions in shaping public discourse and potentially influencing security dynamics, the project integrates advanced word analysis techniques with machine learning algorithms. By leveraging real news data, this hybrid framework seeks to close existing knowledge gaps and provide actionable insights into potential security risks associated with online emotions. By combining analytical methodologies with real-world data, it aims to empower authorities with the tools needed to proactively identify and address emerging security challenges, thereby enhancing political security and national safety in the digital age.
A. Motivation
The motivation behind developing a political security threat prediction framework using a hybrid lexicon machine learning technique lies in its potential to improve accuracy, enhance contextual understanding, enable real-time monitoring, ensure adaptability and scalability, foster interdisciplinary insights, and address ethical considerations in security prediction and intervention.
B. Objective
The objective is to enhance national security by proposing a novel framework for predicting political security threats in cyberspace. This involves combining lexicon-based methods and machine learning, employing Decision Tree, Naive Bayes, and Support Vector Machine classifiers. The goal is to optimize threat detection, with experimental validation revealing the superiority of a hybrid Lexicon-based approach using the Decision Tree classifier. Additionally, exploring Random Forest as an extension showcases improved accuracy in threat prediction through feature optimization.
???????C. Proposed System
In this study, We proposes a new theoretical framework for predicting political security threats using a hybrid technique: the combination of lexicon-based approach and machine learning in cyberspace which are highly related to emotions embedded within the text of online news.
The scope of this research is political security which is a key element of national security. The proposed framework is validated by experimental analysis using the hybrid technique in mining people’s sentiments or opinions, we applied an ensemble method combining the predictions of multiple individual models to produce a more robust and accurate final prediction. Text data was gathered from online news platforms for conducting the experiments.
???????D. Advantages
- Hybrid system blends lexicon-based analysis and advanced machine learning for more comprehensive political security threat prediction.
- Decision Tree, Naive Bayes, and Support Vector Machine improve accuracy, ensuring reliable insights into potential risks.
- Filling gaps in sentiment analysis, the system provides nuanced understanding for better political security risk anticipation and management.
- The hybrid system innovates cybersecurity, addressing drawbacks and offering an advanced tool for predicting and mitigating political security threats in the digital landscape.
II. LITERATURE SURVEY
A. Opinion mining for National Security
It explores the use of opinion mining, specifically sentiment analysis, in the realm of national security. It highlights the significance of extracting public opinions from digital platforms and reviews various techniques such as machine learning, lexicon-based approaches, hybrid methods, and the Kansei approach. The Kansei approach, focusing on sensory-based assessments of human emotions, is proposed as a valuable addition to sentiment analysis in national security contexts. The article emphasizes the need for continual improvement in sentiment analysis techniques to better understand public sentiment on sensitive topics like national security.
B. Sentiment analysis Methods and Approach
The importance of sentiment analysis in decision-making, highlighting its application in various sectors such as business and investment.
It examines different methodologies, including Lexicon-Based and Machine Learning-Based approaches, and addresses challenges in accurately extracting sentiment from text. Overall, it offers a survey of sentiment analysis techniques to aid stakeholders in making informed decisions
III. IMPLEMENTATION
A. Modules
- Data Collection: This component involves gathering textual data from various sources such as news articles, social media feeds, government reports, and academic papers. The data should cover a diverse range of political events, conflicts, and security incidents.
- Data Preprocessing: Preprocessing prepares textual data for analysis by standardizing its format and content. This includes tokenization, stop words removal, punctuation removal, lowercase conversion, and stemming/lemmatization.
- Splitting Data into Train and Test: splitting data into training and testing sets allows for the development of machine learning models that can make accurate predictions or classifications on new, unseen data while providing an objective evaluation of the model's performance.
- Model Generation: Building the model -Naive Bayes -SVM -Decision Tree -Voting CLassifier (AB + RF) -Stacking Classifier, Algorithms accuracy calculated. Using this module will get registration and login and will give input for prediction.
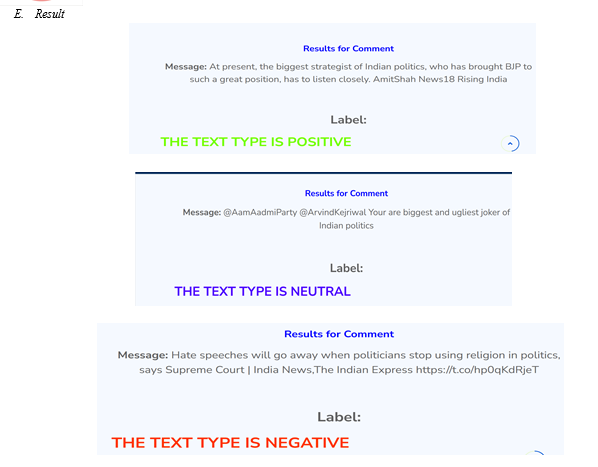
- Prediction: Use the loaded model to make predictions on the new textual data. Feed the extracted features into the model, and the model will output predictions indicating the likelihood or category of political security threats associated with the input text.
???????B. Algorithms
- Naïve Bayes: It is a classification technique based on Bayes' Theorem with an independence assumption among predictors. In simple terms, a Naive Bayes classifier assumes that the presence of a particular feature in a class is unrelated to the presence of any other feature.
- Support Vector Machine: SVM algorithm finds the closest point of the lines from both the classes. These points are called support vectors. The distance between the vectors and the hyperplane is called as margin. And the goal of SVM is to maximize this margin. The hyperplane with maximum margin is called the optimal hyperplane.
- Decision Tree: A decision tree algorithm is a machine learning algorithm that uses a decision tree to make predictions. It follows a tree-like model of decisions and their possible consequences. The algorithm works by recursively splitting the data into subsets based on the most significant feature at each node of the tree.
- Voting Classifier: A Voting Classifier is a machine learning model that trains on an ensemble of numerous models and predicts an output (class) based on their highest probability of chosen class as the output.
- Stacking Classifier: Stacking is an ensemble machine learning algorithm that learns how to best combine the predictions from multiple well-performing machine learning models. The scikit-learn library provides a standard implementation of the stacking ensemble in Python.
???????C. Techniques
- Lexicon Development: Process of creating or compiling a specialized dictionary or vocabulary relevant to a particular domain or application. In the context of the political security threat prediction framework using a hybrid lexicon-machine learning technique, lexicon development involves creating lists of terms and phrases related to political security threats.
- Machine Learning : Supervised Learning Training machine learning model using labeled data, where the models learn patterns and relationships between input features e.g., lexicon-based scores, sentiment analysis results and the target variable e.g., political security threat categories.
- Hybridization: Ensemble Learning Combining predictions from multiple models, each trained using different techniques or subsets of features, to improve overall prediction accuracy.

V. FUTURE WORK
Future efforts enhance emotion detection, exploring nuanced indicators and expanding the emotion lexicon for a more comprehensive understanding of sentiments in textual data .Ensuring system effectiveness in diverse online environments involves adapting it for different domains and languages beyond initial political security applications. Developing real-time threat response mechanisms allows the system to offer timely insights and proactive measures against emerging political security threats in cyberspace. Implementing ongoing model training, informed by evolving data trends and user feedback, is crucial for maintaining system adaptability and enhancing predictive accuracy over time.
Conclusion
Our proposed framework for predicting political security threats using a hybrid approach of lexicon-based analysis and machine learning techniques are designed to analyze people’s opinions on the national security domain, with a specific focus on the political security element. We aims to enhance opinion mining in the national security domain, and it includes opinion mining and national security elements specific to political security to create a multi-research domain study. We successfully demonstrated the relationship between emotions, opinions, sentiment, and political security threats in cyberspace. We presents a new theoretical framework that utilizes the lexicon-based approach and machine learning for the emotional assessment of text in the national security domain, specifically for the political security element. We concludes that the combination of the lexicon-based approach with the decision tree classifier is the best hybrid approach method for detecting political security threats based on emotions embedded within online news text. As future work, a performance analysis of the proposed method using a massive dataset for this method will be conducted.
References
[1] J. R. Clapper, ‘‘Statement for the record: Worldwide threat assessment of the us intelligence community,’’ Office Director Nat. Intell., Congressional Testimonies 2015, USA, 2015. [Online]. Available: https://www.dni.gov/files/SFR-DirNCTCSHSGACHearing8Oct.pdf [2] N. A. M. Razali et al., ‘‘Opinion mining for national security: Techniques, domain applications, challenges and research opportunities,’’ J. Big Data, vol. 8, no. 1, 2021, doi: 10.1186/s40537-021-00536-5. [3] S. Dorle, ‘‘Sentiment analysis methods and approach: Survey,’’ Int. J. Innov. Comput. Sci. Eng., vol. 4, no. 6, pp. 1–5, Dec. 2017, [Online]. Available: http://www.ijicse.in/index.php/ijicse/article/view/134 [4] A. Balahur, R. Steinberger, E. Van Der Goot, B. Pouliquen, and M. Kabadjov, ‘‘Opinion mining on newspaper quotations,’’ in Proc. IEEE/WIC/ACM Int. Joint Conf. Web Intell. Intell. Agent Technol., Sep. 2009, pp. 523–526, doi: 10.1109/WI-IAT.2009.340. [5] B. Seerat, ‘‘Opinion mining: Issues and challenges(A survey),’’ Int. J. Comput. Appl., vol. 49, no. 9, pp. 42–51, 2012, doi: 10.5120/7658-0762. [6] P. Barnaghi, J. G. Breslin, I. D. A. B. Park, and L. Dangan, ‘‘Opinion mining and sentiment polarity on Twitter and correlation between events and sentiment,’’ in Proc. IEEE 2nd Int. Conf. Big Data Comput. Service Appl. (BigDataService), Mar./Apr. 2016, pp. 52–57, doi: 10.1109. [7] K. Ravi and V. Ravi, ‘‘A survey on opinion mining and sentiment analysis: Tasks, approaches and applications,’’ Knowl.-Based Syst., vol. 89, pp. 14–46, Nov. 2015. [8] G. Isabelle, W. Maharani, and I. Asror, ‘‘Analysis on opinion mining using combining lexicon-based method and multinomial Naïve Bayes,’’ in Proc. Int. Conf. Ind. Enterprise Syst. Eng., vol. 2, 2019, pp. 214–219, doi: 10.2991/icoiese-18.2019.38. [9] H. Zhang, W. Gan, and B. Jiang, ‘‘Machine learning and lexicon based methods for sentiment classification: A survey,’’ in Proc. 11th Web Inf. Syst. Appl. Conf., Sep. 2014, pp. 262–265, doi: 10.1109/WISA.2014.55. [10] M. P. Ashna and A. K. Sunny, ‘‘A study on sentiment analysis in Malayalam language,’’ Int. J. Adv. Res. Comput. Commun. Eng., vol. 6, no. Special Issue 3, pp. 88–93, 2017, doi: 10.17148/IJARCCE.
Copyright
Copyright © 2024 N. Bhagyalakshmi, V. Keerthi Priya, P. Divya, V. Rebka. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

Download Paper
Paper Id : IJRASET58781
Publish Date : 2024-03-05
ISSN : 2321-9653
Publisher Name : IJRASET
DOI Link : Click Here
 Submit Paper Online
Submit Paper Online

